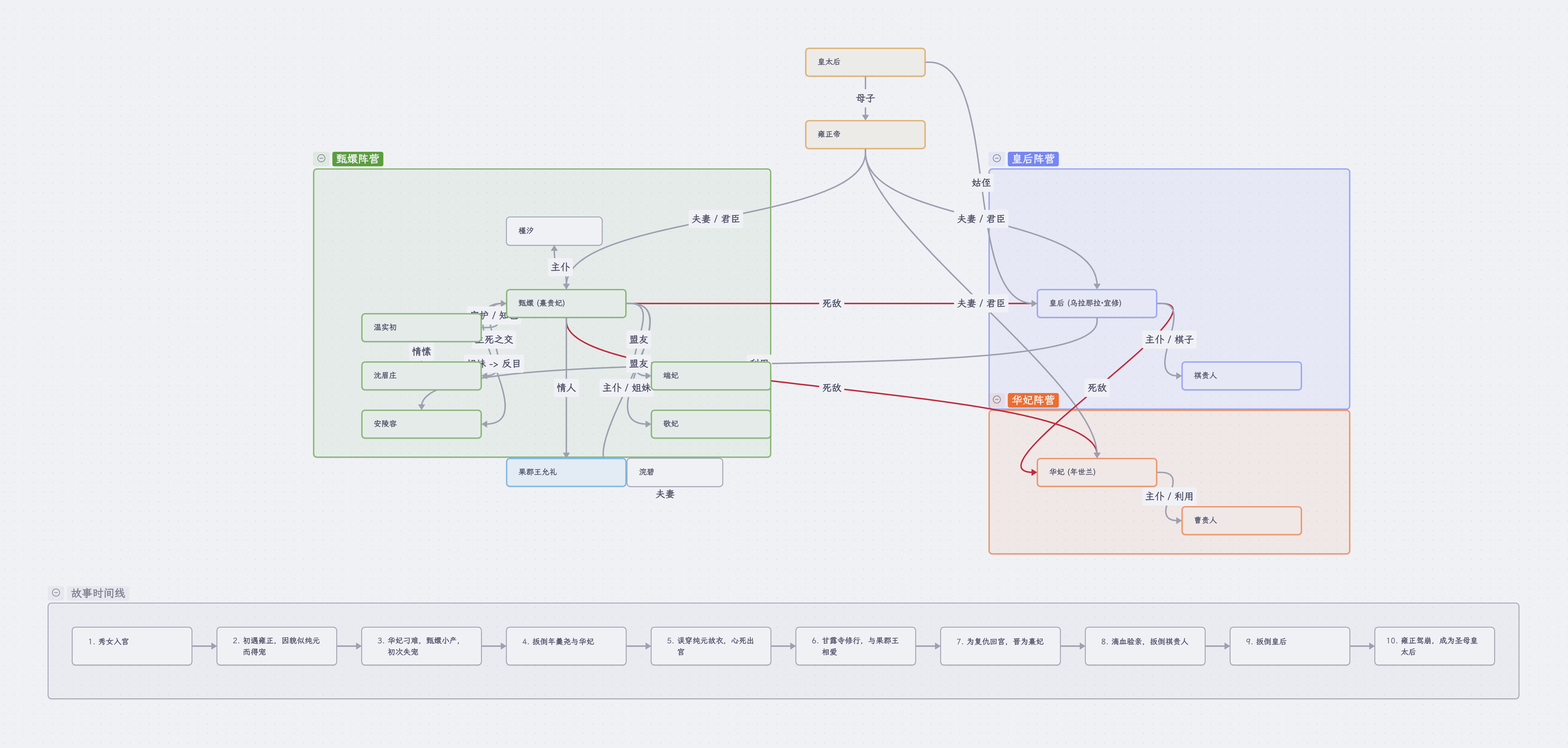
示例一
无中生有,直接一句话让cursor生成canvas。
生成甄嬛传人物关系图和时间线 canvas这里我之所以可以写这么短的提示词,是因为使用了cursorrule,里面已经有比较详细的提示词描述了,全文见文末。
生成效果:
示例二
基于仓库内已存在的文档,让cursor分析汇总,并生成canvas,这样做的好处是,会引用仓库已有的文件,而不是单纯生成卡片。方便我们做二次修改和加工。详见cursor 引用Obsidian 知识库文件生成 canvas的提示词。
经验
模型gemini-2.5-pro表现稳定,但会忘记text内的”引号转义。如果canvas打不开,提醒他转义既可。已经直接写到cursorrule中。
cloude 4 sonnet 模型会用Obsidian advanced canvas 规范中的各种高级节点类型(菱形、圆形等),但显得不美观,审美一般。
o3模型生成的会比较简单,可能是提示词给的太简短。
cursorrules
2025-06-27更新:my-obsidian-rules.mdc,全文:
# Obsidian 数字花园 Cursor Rule
## 1. 总览与定位
- 本仓库为个人 Obsidian 数字花园,核心理念为"原子化笔记、双链、MOC(Map of Content) 导航、动态索引"。
- 采用 Zettelkasten、ACCESS目录结构、PARA 等 PKM 方法论,强调知识网络与持续进化。
- 结构与工作流详见 @🧰 本库使用指南.md 。
## 2. 目录结构约定
- `🍀 花园导览/`:知识库导航入口、MOC、结构说明、方法论、发布指南等。
- `📥 Inbox/`:收集箱,临时笔记、灵感、待整理内容。
- `Atlas/`:核心知识区,包含 Canvas(可视化)、Dataviews(动态索引)、Draws(绘图)等。详见 @Atlas.md。
- `Cards/`:卡片笔记区,存放原子化的永久笔记。
- `Calendar/`:日历区,包含每日笔记、周报、月报、年报等。
- `Extras/`:附加区,包含文档、媒体、模板、软件配置等。
- `Sources/`:外部资料区,包含文章、书籍、剪藏等。
- `Spaces/`:特定领域或项目的工作空间,使用 @PARA.md组织,例如 `Spaces/0-Project/` 用于项目管理。详见 @Projects Readme.md 。
## 3. 文件命名与内容规范
- 支持 Obsidian 的 `[[双链]]`、`#标签`、YAML frontmatter 头信息(如 title、tags、filetype、data created 等)。
- 永久笔记应原子化表达一个核心思想,临时/文献/索引笔记分开管理并互链。
- 如果完全从0开始生成一个新文件,则记得加上 frontmattert字段: `tags: [AI生成]`,注意使用数组格式。
- 当你创建新的md文档,需要引用其他md文件时,记得直接使用最简洁的[[]]语法。
- 必要的时候,请递归访问[[]]引用的文档,继续阅读,获取更多信息。
## 4. 插件与自动化
- 推荐插件:Dataview(动态索引/查询)、Canvas、Calendar、Tag Pane 等。
- Dataview 查询集中存放于 @Atlas/Dataviews/+ Dataviews Readme.md。
- 支持 YAML 属性、自动化索引、任务/项目追踪。
- dataview和datacore暂时先不用,因为现在官方出了@∑ BASE.md插件,可以完全平替掉dataview。
- Base数据库语法见 @Bases syntax.md和 @Bases Functions.md。
## 5. 工作流与方法论
- 参考 ACCESS、PARA、CODE 等 PKM 流程。
- 日常流程:收集(Inbox/Sources/Clippings)→ 处理(整理/转化为永久笔记)→ 链接(建立关联)→ 索引(MOC/Dataview)→ 回顾(定期复习/优化)。
- 强调链接优先,鼓励笔记间多建立双链,形成知识网络。双链的语法是`[[]]`。所以当有必要生成多个md文件的时候,请务必使用双链语法,将多个文件串联。倾向于尽可能地使用[[]]语法,引用已经存在的文档(md、canvas、base、excalidraw等均可),当然不要瞎编不存在的文档。
- 详见 @∑ 本库 ACCESS 工作流汇总.md 。
## 6. 兼容性与开放性
- 纯 Markdown 语法,兼容 Obsidian、VSCode和Cursor(需 foam 插件)等。
- 支持 frontmatter YAML 头信息,便于自动化处理和插件扩展。
- 结构开放,便于迁移、发布、二次开发。
## 7. Obsidian Canvas 规范(JSON Canvas 1.0 简要说明)
- Obsidian Canvas 文件,由于使用了Advanced Canvas插件 ,所以遵循 @Obsidian advanced canvas 规范.md 。
- 主要结构:
- `nodes`:节点数组,支持 text(文本)、file(文件/图片)、link(外链)、group(分组)等类型。
- `edges`:边数组,连接节点。
- 主要字段:
- 节点(node):`id`(唯一标识,不能有`-`短横杆)、`type`、`x`、`y`、`width`、`height`、`color`(可选)、type-specific 字段(如 text、file、url、label 等)。file可以引用其他除了md以外的canvas、bases、excalidraw等文件
- 边(edge):`id`、`fromNode`、`toNode`、`fromSide`/`toSide`(可选)、`fromEnd`/`toEnd`(可选)、`color`(可选)、`label`(可选)。
- 颜色(color):支持 hex 代码或 1-6 预设色(1=红,2=橙,3=黄,4=绿,5=青,6=紫)。
- **重要提醒:** 在 `nodes` 的 `text` 字段中,如果文本内容本身包含双引号 (`"`),必须使用反斜杠 (`\`) 进行转义,即写为 `\"`,以确保 JSON 格式的有效性。如果要换行,则需要在每行末尾加2个空格再用\n换行的markdown严格换行模式。生成canvas的node时,需要依据text文本长度,给一个合适的width、x、y的值。Obsidian advanced canvas 规范
我的额外补充说明:
1. id不允许出现短横杆`-`。
2. shape 尽量少用,因为它会导致卡片文本显示不全。
以下是Obsidian advanced canvas 规范:
# Advanced JSON Canvas Spec
<small>Version <code>1.0-1.0</code> — 2025-04-30</small>
You can find the TypeScript typings [here](1.0%20(1.0).d.ts).
## Top level
The top level of JSON Canvas contains two arrays:
- `metadata` (optional, object)
- `nodes` (optional, array of nodes)
- `edges` (optional, array of edges)
## Metadata
The metadata object contains metadata about the canvas like the format version and frontmatter attributes.
The metadata object includes the following attributes:
- `version` (required, string) is the version of the Advanced JSON Canvas format.
- `1.0-1.0` is the only valid value in this version.
- `frontmatter` (optional, object) is a JSON object containing frontmatter attributes. The frontmatter object can contain any number of key-value pairs. The keys must be strings, and the values can be strings, numbers, booleans, or arrays. The frontmatter object is used to store metadata about the canvas.
- `startNode` (optional, string) is the ID of the node that is the starting point of the canvas. Currently used for the starting point of a presentation.
The metadata object also supports arbitrary attributes. Keep in mind: All metadata object attributes should relate to the canvas as a whole, not to individual nodes or edges.
## Nodes
Nodes are objects within the canvas. Nodes may be text, files, links, or groups.
Nodes are placed in the array in ascending order by z-index. The first node in the array should be displayed below all other nodes, and the last node in the array should be displayed on top of all other nodes.
### Generic node
All nodes include the following attributes:
- `id` (required, string) is a unique ID for the node.
- `type` (required, string) is the node type.
- `text`
- `file`
- `link`
- `group`
- `x` (required, integer) is the `x` position of the node in pixels.
- `y` (required, integer) is the `y` position of the node in pixels.
- `width` (required, integer) is the width of the node in pixels.
- `height` (required, integer) is the height of the node in pixels.
- `dynamicHeight` (optional, boolean) is whether the node has a dynamic height. If true, the height of the node will be determined by its content. Defaults to `false`.
- `ratio` (optional, float) is the aspect ratio of the node. When defined, the node will maintain this aspect ratio when resized. The ratio is calculated as `width / height`.
- `color` (optional, `canvasColor`) is the color of the node, see the Color section.
- `styleAttributes` (optional, object) is a JSON object containing style attributes. The style attributes can contain any number of key-value pairs. The keys must be strings, and the values can be strings, numbers, booleans, or arrays. The style attributes are used to store additional styling information about the node. Supported style attributes include, but are not limited to:
- `textAlign` (optional, string) is the text alignment of the node. If not specified, the default alignment is `left`. Valid values:
- `left`
- `center`
- `right`
- `shape` (optional, string) is the shape of the node. If not specified, the default shape is `rectangle`. Valid values:
- `rectangle`
- `pill`
- `diamond` (Rhombus-shaped)
- `parallelogram`
- `circle`
- `predefined-process` (Rectangle with double lines on the sides)
- `document` (Rectangle with a wavy bottom edge)
- `database` (Cylinder)
- `border` (optional, string) is the border style of the node. If not specified, the default border is `solid`. Valid values:
- `solid`
- `dashed`
- `dotted`
- `invisible` (No border as well as no background color)
### Text type nodes
Text type nodes store text. Along with generic node attributes, text nodes include the following attribute:
- `text` (required, string) in plain text with Markdown syntax.
### File type nodes
File type nodes reference other files or attachments, such as images, videos, etc. Along with generic node attributes, file nodes include the following attributes:
- `file` (required, string) is the path to the file within the system.
- `subpath` (optional, string) is a subpath that may link to a heading or a block. Always starts with a `#`.
- `portal` (optional, boolean) is whether the file node is a portal. If true, the file node will be displayed as a portal to the file. See the Portal section for more information.
- `interdimensionalEdges` (optional, array of edges) is an array of edges that connect a node from the current canvas to a node from the portal canvas. The edges are stored in the `interdimensionalEdges` object. Each edge is an object. For more information, see the Edges section.
### Link type nodes
Link type nodes reference a URL. Along with generic node attributes, link nodes include the following attribute:
- `url` (required, string)
### Group type nodes
Group type nodes are used as a visual container for nodes within it. Along with generic node attributes, group nodes include the following attributes:
- `label` (optional, string) is a text label for the group.
- `background` (optional, string) is the path to the background image.
- `backgroundStyle` (optional, string) is the rendering style of the background image. Valid values:
- `cover` fills the entire width and height of the node.
- `ratio` maintains the aspect ratio of the background image.
- `repeat` repeats the image as a pattern in both x/y directions.
- `collapsed` (optional, boolean) is whether the group is collapsed. If true, only the label is shown.
## Edges
Edges are lines that connect one node to another.
- `id` (required, string) is a unique ID for the edge.
- `fromNode` (required, string) is the node `id` where the connection starts.
- `fromSide` (required, string) is the side where this edge starts. Valid values:
- `top`
- `right`
- `bottom`
- `left`
- `fromFloating` (optional, boolean) is whether the edge is floating. If true, the connection side is determined by the shortest distance to the `toNode`. Defaults to `false`.
- `fromEnd` (optional, string) is the shape of the endpoint at the edge start. Defaults to `none` if not specified. Valid values:
- `none`
- `arrow`
- `toNode` (required, string) is the node `id` where the connection ends.
- `toSide` (required, string) is the side where this edge ends. Valid values:
- `top`
- `right`
- `bottom`
- `left`
- `toFloating` (optional, boolean) is whether the edge is floating. If true, the connection side is determined by the shortest distance to the `fromNode`. Defaults to `false`.
- `toEnd` (optional, string) is the shape of the endpoint at the edge end. Defaults to `arrow` if not specified. Valid values:
- `none`
- `arrow`
- `color` (optional, `canvasColor`) is the color of the line, see the Color section.
- `label` (optional, string) is a text label for the edge.
- `styleAttributes` (optional, object) is a JSON object containing style attributes. The style attributes can contain any number of key-value pairs. The keys must be strings, and the values can be strings, numbers, booleans, or arrays. The style attributes are used to store additional styling information about the edge. Supported style attributes include, but are not limited to:
- `path` (optional, string) is the style of the line. Defaults to `solid` if not specified. Valid values:
- `solid`
- `long-dashed`
- `short-dashed`
- `dotted`
- `arrow` (optional, string) is the style of the arrow. Defaults to `triangle` if not specified. Valid values:
- `triangle`
- `triangle-outline`
- `thin-triangle` (Just the two lines of the triangle >)
- `halved-triangle` (Triangle, but only one side is filled)
- `diamond` (Rhombus-shaped)
- `diamond-outline`
- `circle`
- `circle-outline`
- `blunt` (90-degree angled line)
- `pathfindingMethod` (optional, string) is the method used to calculate the path of the edge. Defaults to `bezier` if not specified. Valid values:
- `bezier`
- `direct`
- `square` (Right-angled lines)
- `a-star` (A* pathfinding algorithm)
## Color
The `canvasColor` type is used to encode color data for nodes and edges. Colors attributes expect a string. Colors can be specified in hex format e.g. `"#FF0000"`, or using one of the preset colors, e.g. `"1"` for red. Six preset colors exist, mapped to the following numbers:
- `"1"` red
- `"2"` orange
- `"3"` yellow
- `"4"` green
- `"5"` cyan
- `"6"` purple
While 1-6 are predefined by the application, the user can define their own preset colors that are mapped to the numbers higher than 6. There is no way for the application to know what color is mapped to a number higher than 6, so the application either needs to treat it like no color or allow the user to define the color in the application settings.
Specific values for the preset colors are intentionally not defined so that applications can tailor the presets to their specific brand colors or color scheme.
## Portal
Portals are a special type of file node that allow you to embed another canvas within the current canvas. Portals don't need to be interactive, but they can be. Edges between portal nodes and nodes within the host canvas are supported and stored in the `interdimensionalEdges` object.